A comprehensive transferability evaluation of U-Net and ResU-Net for landslide detection from Sentinel-2 data (case study areas from Taiwan, China, and Japan)
Citation
Ghorbanzadeh, O., Crivellari, A., Ghamisi, P., Shahabi, H., Blaschke, T. (2021). A comprehensive transferability evaluation of U-Net and ResU-Net for landslide detection from Sentinel-2 data (case study areas from Taiwan, China, and Japan). Scientific Reports, 11: 14629. Link to paper
Abstract
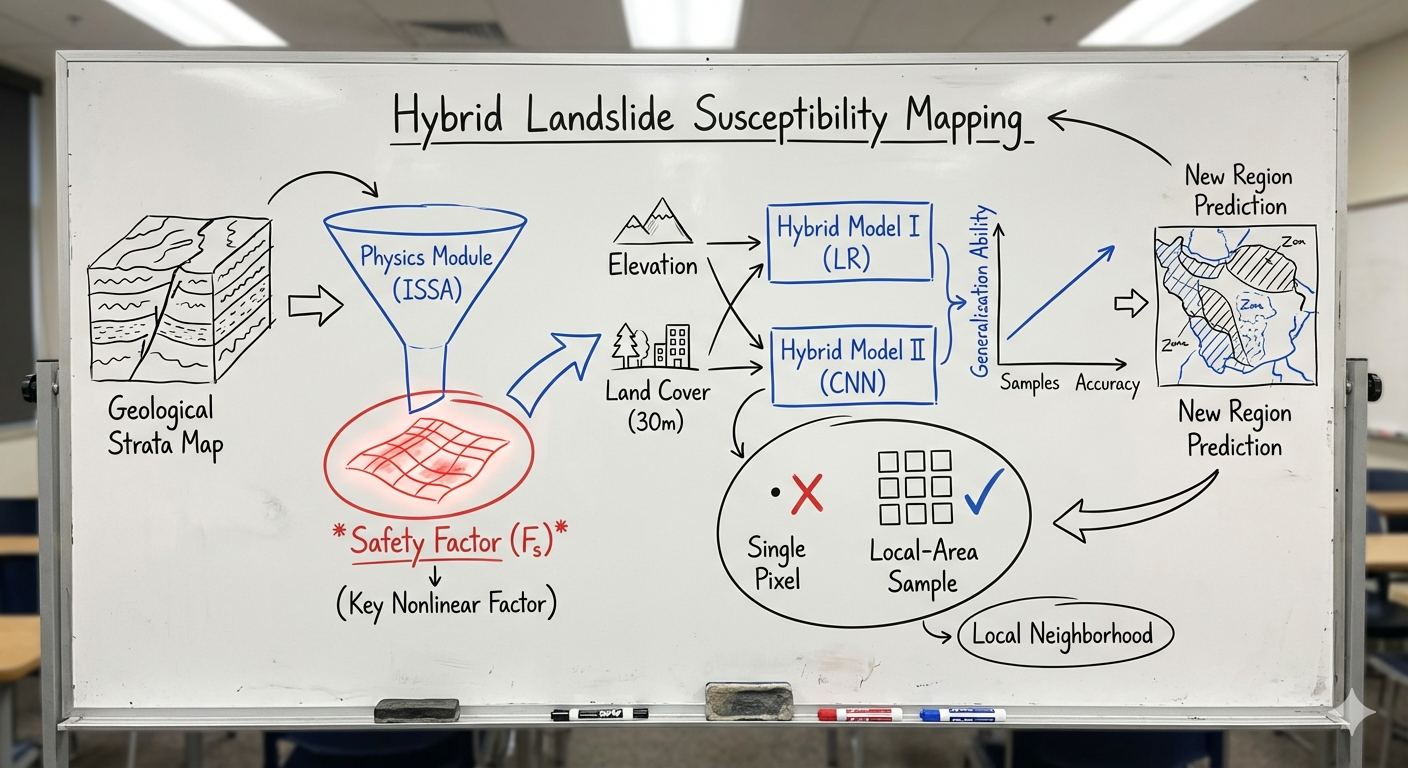
This study showcases the potential of U-Net and ResU-Net architectures for landslide detection from freely available Sentinel-2 optical data and ALOS digital elevation model (DEM). The research evaluates the impact of different sample patch window sizes on detection accuracy and assesses cross-regional transferability performance using three case study areas: Western Taitung County (Taiwan), Shuzheng Valley (China), and Eastern Iburi (Japan). The highest F1-score of 73.32% was obtained by ResU-Net trained with a dataset from Japan and tested on China's holdout testing area using a sample patch size of 64×64 pixels. This represents the first application of fully convolutional networks for landslide detection using only freely available satellite data. The transferability analysis reveals that models trained in one region can successfully detect landslides in geographically and geologically distinct areas, though performance varies based on the similarity of landslide characteristics and environmental conditions. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of developing global landslide detection models that can be applied across diverse regions without requiring extensive local training data.
AI Visual Interpretation (Beta)